Java Language Roadmap: From Basics to Advanced
Introduction
The Java language is one of the most widely used programming languages in the world. From Android apps to enterprise-level web applications, Java powers a significant portion of modern software. Whether you’re a complete beginner or aiming to become a backend developer, this comprehensive roadmap will guide you from the basics to advanced topics in a structured, easy-to-follow way.
[The Resources are provided at the end of the page]
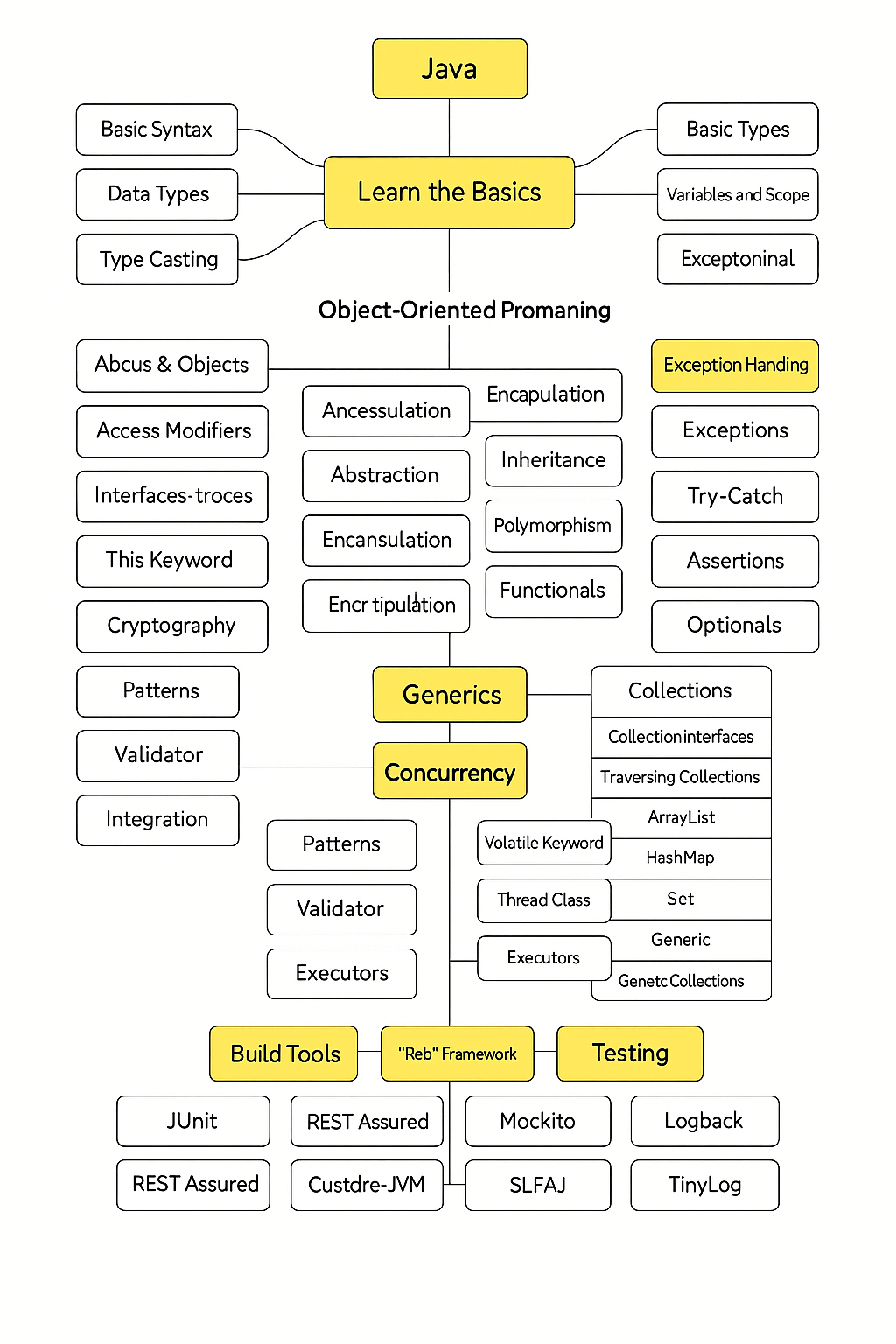
🧱 1. Learn the Basics of Java Language
Start with the fundamentals. These are the foundation of everything you’ll build in Java.
- What is Java?
- Installing JDK and setting up your development environment (like IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse)
- Writing your first Java program (Hello World)
- Java syntax and structure
- Data types and variables
- Operators and expressions
- Input and output using
Scanner
Understanding these core concepts is the first step to becoming comfortable with the Java language.
🔄 2. Master Control Flow and Loops
Control flow allows your program to make decisions and repeat actions.
if,else if, andelsestatementsswitchstatement- Loops:
for,while,do-while - Loop control:
break,continue
Mastering control flow will enable you to write logic-driven applications using the Java language.
📦 3. Dive into Functions and Methods
Functions (called methods in Java) help break your code into reusable blocks.
- Declaring and calling methods
- Method parameters and return types
- Method overloading
- The
main()method structure in Java
Clear understanding of methods is essential for writing modular, maintainable code.
🧰 4. Learn Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Java is built on OOP principles. This is where the Java language really shines.
- Classes and Objects
- Constructors
thiskeyword- Inheritance and polymorphism
- Encapsulation and abstraction
- Access modifiers (
public,private,protected) - Method overriding
These principles allow you to design and build scalable, reusable code structures.
📚 5. Work with Java Collections and Arrays
Data handling is a core part of programming. Learn how to store and manipulate groups of data.
- Arrays
- ArrayLists, LinkedLists
- HashMaps, HashSets
- Iterators and enhanced
forloop
Collections in Java are optimized and highly used in real-world applications.
🧪 6. Exception Handling and File I/O
Write programs that can handle unexpected situations without crashing.
- Try-Catch blocks
- Finally throw keywords
- Custom exceptions
- Reading and writing files using
FileReader,BufferedReader,FileWriter, etc.
This part of the Java language is key for developing robust, real-world applications.
🧩 7. Learn Java Libraries and Frameworks
Once your core knowledge is solid, start exploring powerful libraries and frameworks:
- For Web Development: Spring Boot, Java EE
- For GUI Applications: JavaFX, Swing
- For Testing: JUnit
- For JSON handling: Gson, Jackson
Understanding how to use libraries saves time and adds powerful capabilities to your apps.
⚙️ 8. Multithreading and Concurrency
Java is known for its strong multithreading capabilities.
- Threads and the
Runnableinterface - Thread lifecycle and synchronization
ExecutorService, and thread pools
If you’re building high-performance apps, this is a must-know area in the Java language.
🧑💻 9. Build Real-World Projects
Apply what you’ve learned by building projects:
- Student management system
- Expense tracker
- CRUD application with Java and MySQL
- Simple game (like Tic Tac Toe or Snake)
- Spring Boot REST API
Projects strengthen your knowledge and are great additions to your portfolio.
📈 10. Explore Advanced Java Topics
If you’re ready for more advanced concepts, dig deeper into:
- Java Generics
- Lambda Expressions and Streams
- Functional Interfaces
- Annotations and Reflection API
- Java Design Patterns
- JVM internals and garbage collection
These topics are often used in interviews and large-scale Java projects.
✅ Conclusion
The Java language offers a stable and versatile platform to build almost anything, from desktop software to mobile apps and backend systems. Following this roadmap, you can learn Java systematically, sharpen your problem-solving skills, and become job-ready. Take time, practice regularly, and build real projects to reinforce your learning.
Resources:
YouTube Channels:
English language- BRO CODE (Click on the names to visit the YouTube video)
Telugu Language- Telusuko
Hindi Language- Complete Coding by Prashant Sir
Websites to Learn:
2. Code Academy
